Annotations in Typed Clojure are essential, but tedious to write. We need a tool to generate type annotations automatically, based on the specifications we already give via tests.
In this post, I set the stage for why this tool is necessary. We discuss how it
- provides valuable generated documentation at any point in the development cycle,
- assists in the effort to generate contracts for untyped code to participate in gradual typing, and
- helps static type checking by reducing the annotation effort.
This work is part of a crowdfunding effort, please support the campaign here!
The Annotation Burden
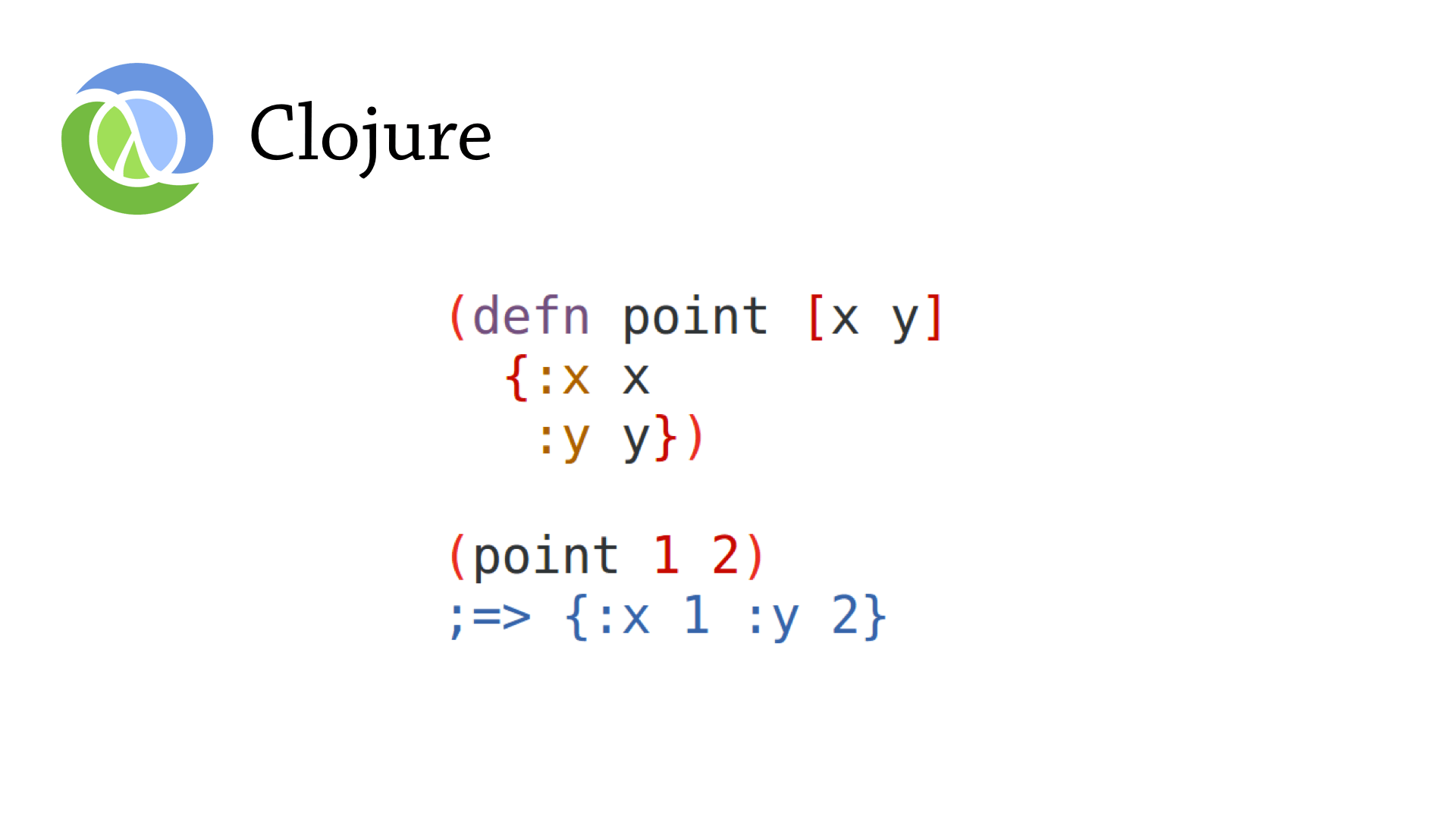
Below is a
function written in Clojure. It creates a point
hash-map that acts as a record.
Here is the same function in Typed Clojure.
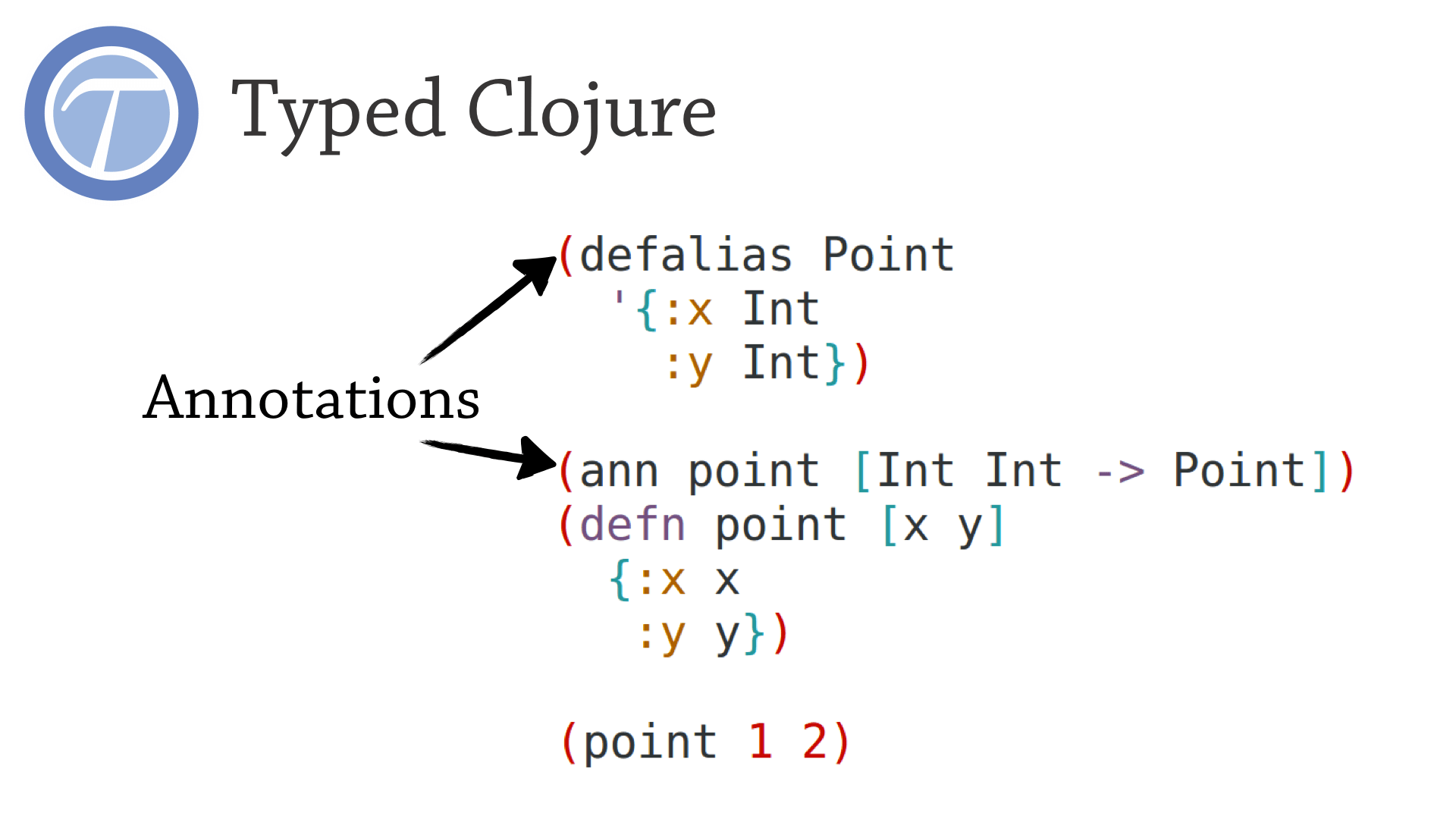
The only difference between the typed and untyped code is annotations. Most effort in porting to Typed Clojure is spent manually creating these annotations.
Why Automatic Annotations?
There are many motivations for automatic type annotations. Here are three.
The first motivation is automatic documentation for partial programs.
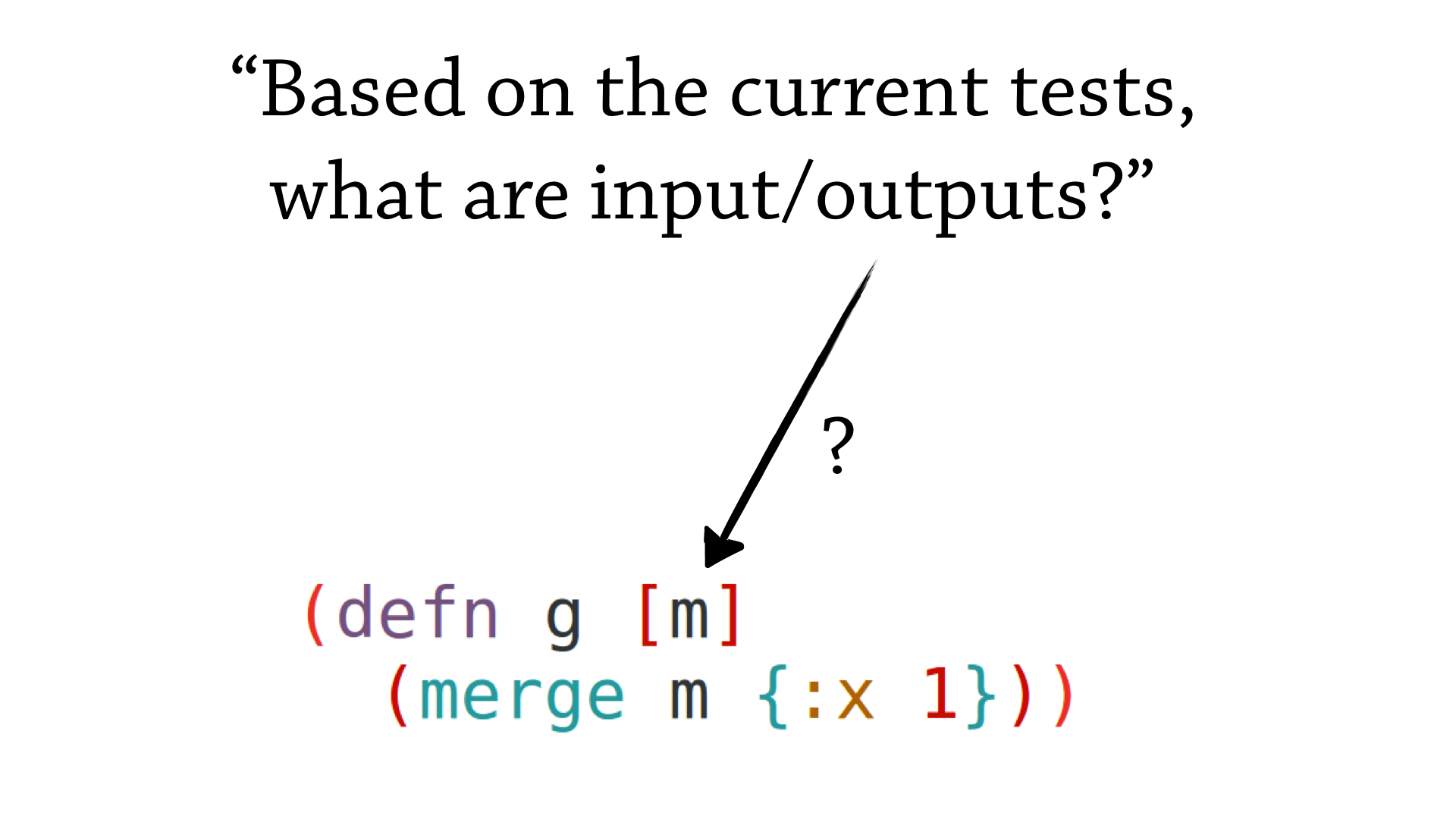
The REPL-driven style of Clojure development often leaves our functions in unfinished states. Using TDD means we exercise the paths of code we are interested in, and summaries of these types in annotations at any time can help write consistent code.

The second motivation is runtime checking.
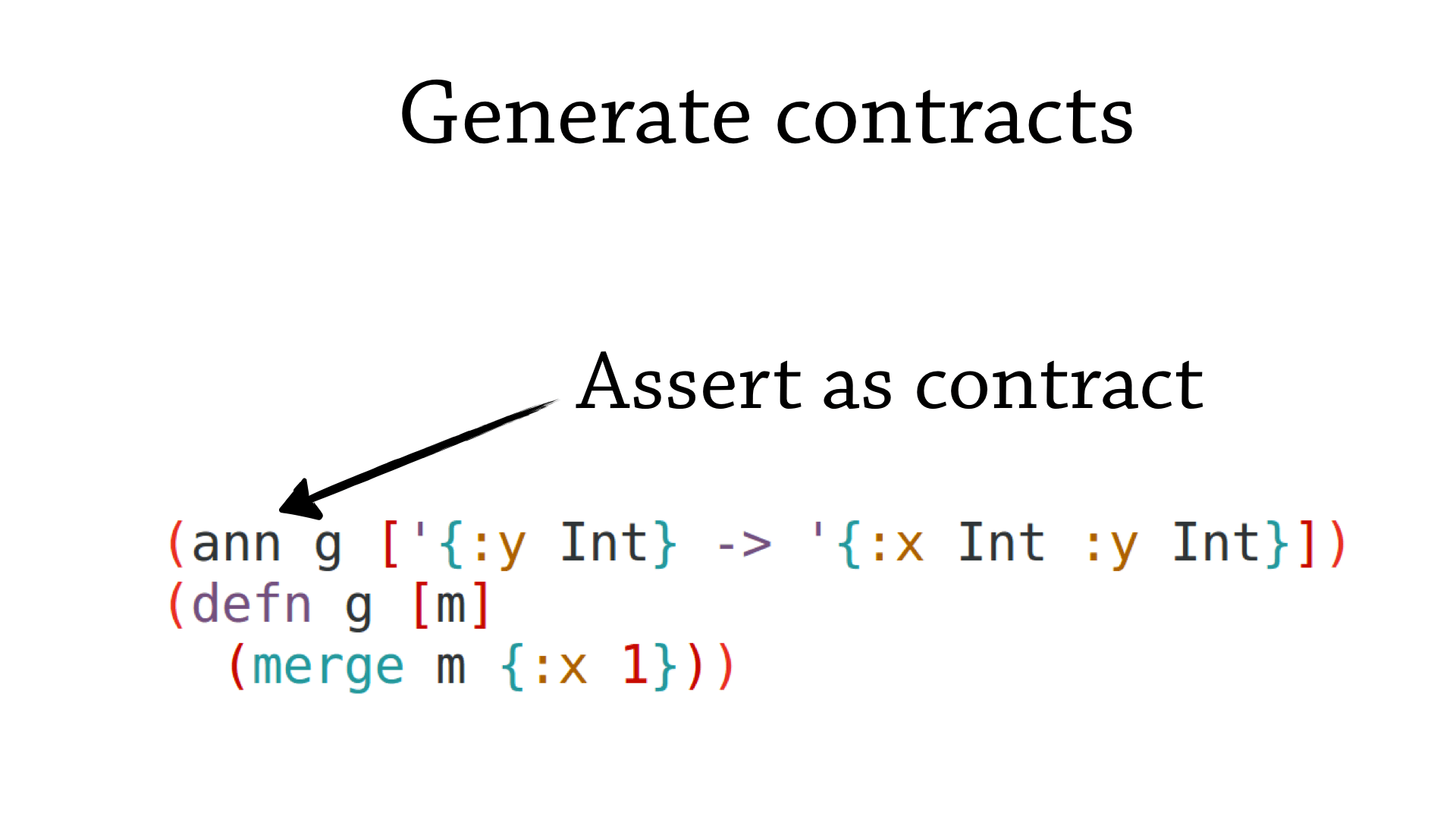
Using the infrastructure developed for gradual typing</a>, we can use annotations to assert runtime contracts.
Gradual typing allows us to treat untyped code as safe when passed to typed code, since a runtime contract violation will prevent ill-typed operations.
The third motivation is fuel for type checking. Type annotations are needed to help the type system use local, instead of global, reasoning to type check code. This is the main spark for this project.
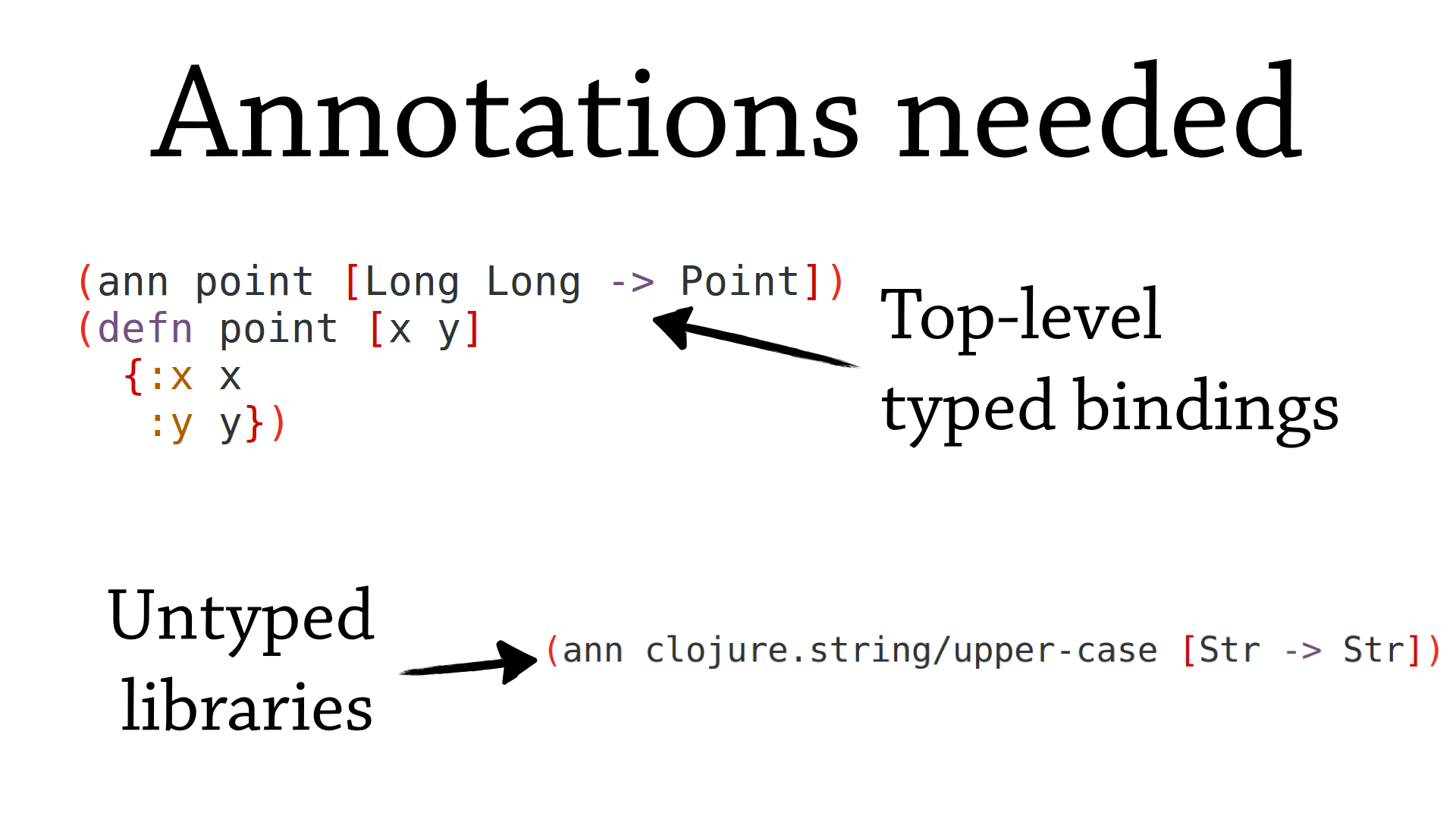
Of the two main kinds of annotations needed, library annotations are the most annoying. Each library function used requires an annotation.
Interestingly, these annotations do not need to be 100% accurate to be useful.
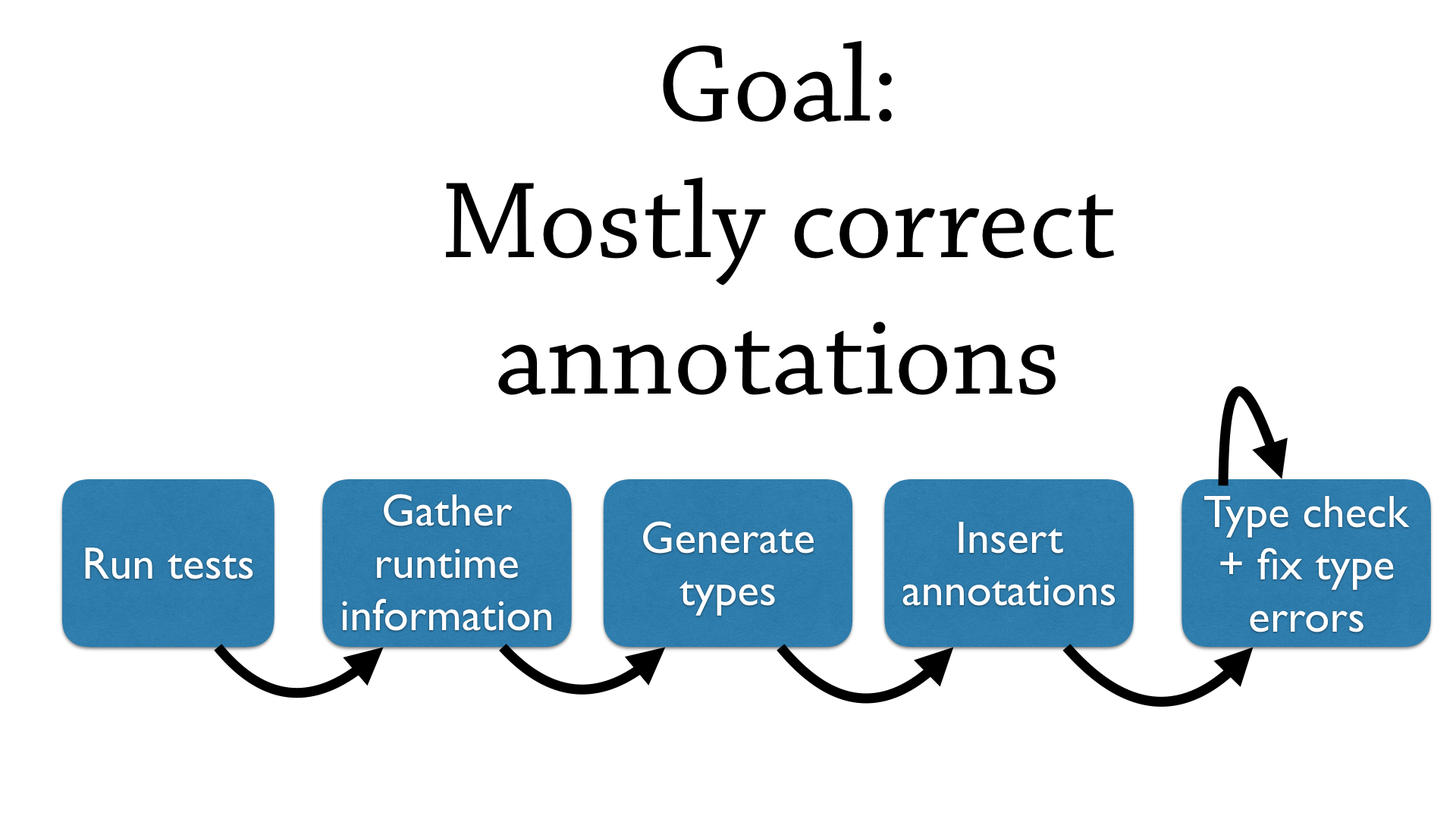
We generate ‘mostly correct’ annotations, and fixing these types is part of the workflow. Simple functions will successfully type check with the generated annotations, and more complicated functions will present you with a mostly complete annotation.
Introducing Automatic Annotations
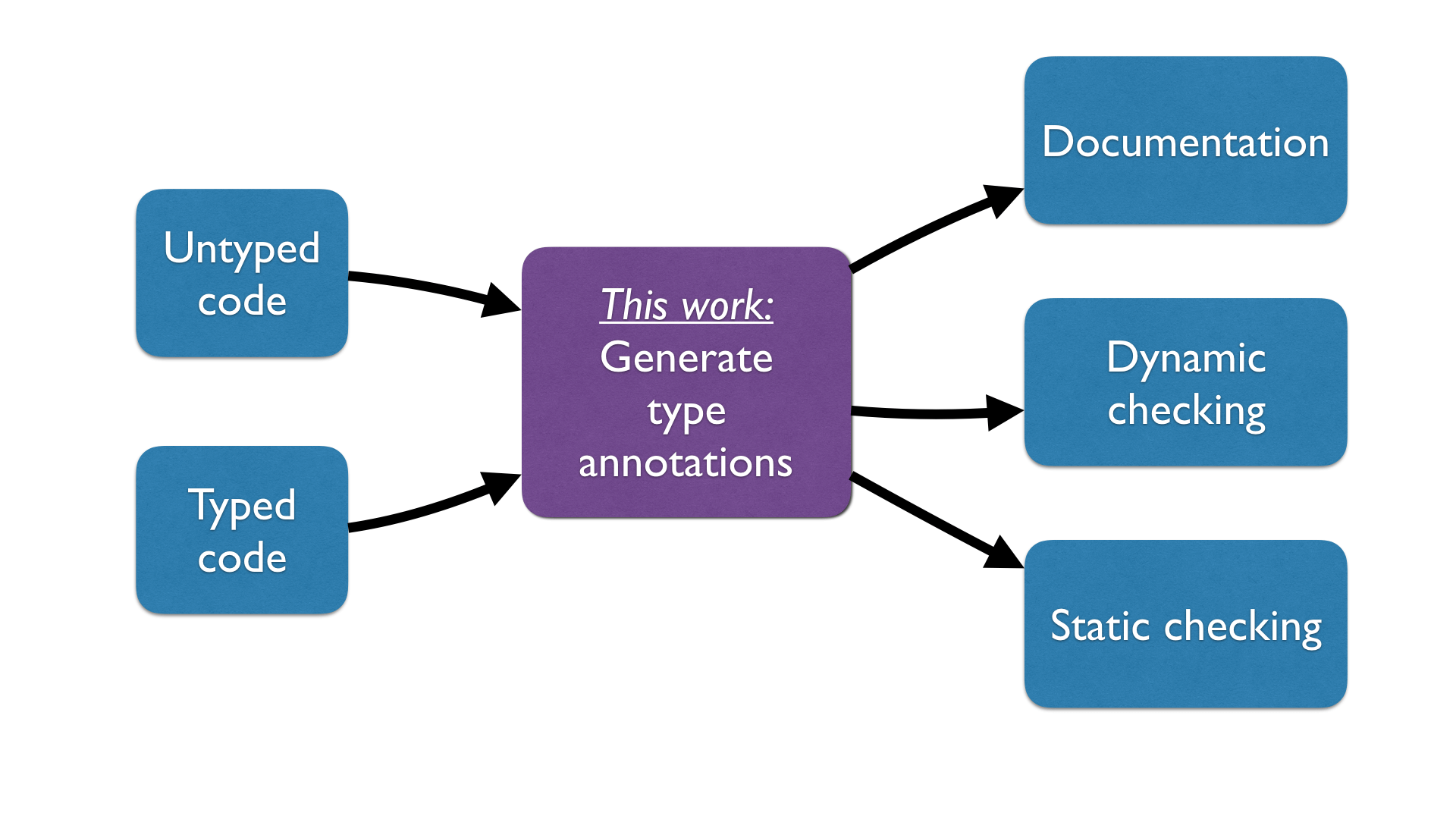
Our automatic annotator generates types that are useful to document and verify (typed or untyped) code, using either runtime or compile-time techniques.
Next posts
That wraps up my introduction to automatic annotations
for Typed Clojure.
Upcoming posts will discuss implementation strategies,
generating clojure.spec types (Write Unit Tests, Get Generative Tests!)
and unique annotation problems related to how Clojure programmers
use data.
If you enjoyed this post, please consider donating to the campaign!